ANDA Submissions: Guidance, Process & Requirements
-
By DocShifter
- 16 minutes read
An example that everyone would recognize is Ibuprofen. Ibuprofen is the generic drug of a brand-name drug (Advil by Pfizer).
This distinction is crucial: NDAs involve extensive clinical trials to establish a drug’s safety and efficacy for the first time. ANDAs on the other hand rely on the existing data for the brand-name drug (called the reference listed drug, or RLD) to demonstrate bioequivalence, meaning the generic version delivers the same amount of medication to the bloodstream in the same way as the RLD.
In simpler terms, an ANDA demonstrates that a generic drug is safe, effective, and essentially therapeutically equivalent to its brand-name counterpart. This stringent process, overseen by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), ensures patients have access to high-quality, more affordable medication.
In this guide, you will find the following information regarding ANDA submissions:
- What ANDAs are and how they differ from NDAs
- The key steps involved in the ANDA submission process
- The importance of ANDAs in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries
By understanding ANDA submissions, we will be able to better understand how generic drugs reach patients and contribute to a more accessible, affordable healthcare system.
Understanding Abbreviated New Drug Applications (ANDAs)
Why are ANDAs crucial? Where do they differ from NDA submissions? What are the essential components of an ANDA submission package? We will explore the answers to these questions in this section. Let’s start with the first one.
Importance of ANDAs in the Pharmaceutical Industry
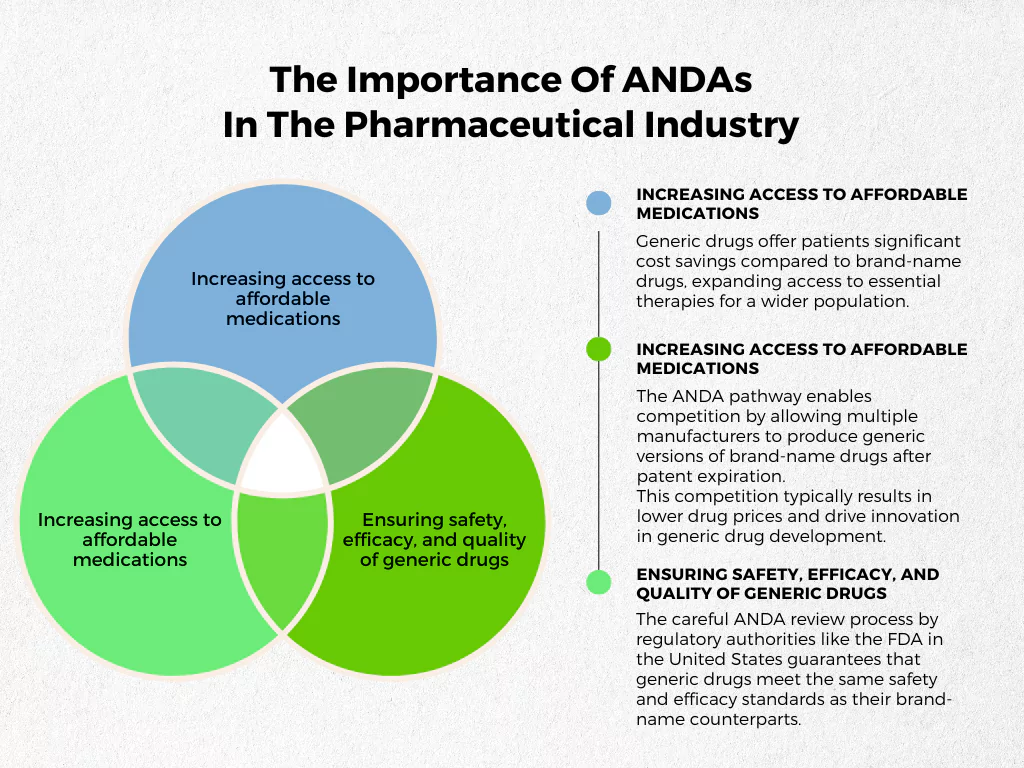
ANDA submissions play a critical role in the pharmaceutical industry (and for the patients) by:
- Increasing access to affordable medications: Generic drugs offer patients significant cost savings compared to brand-name drugs, expanding access to essential therapies for a wider population.
- Facilitating competition in the pharmaceutical market: The ANDA pathway enables competition by allowing multiple manufacturers to produce generic versions of brand-name drugs after patent expiration. This competition typically results in lower drug prices and drive innovation in generic drug development.
- Ensuring safety, efficacy, and quality of generic drugs: The careful ANDA review process by regulatory authorities like the FDA in the United States guarantees that generic drugs meet the same safety and efficacy standards as their brand-name counterparts.
What are the differences between ANDA & NDA submissions?
The key distinction lies in the purpose and level of data required for each application:
| Feature | NDA (New Drug Application) | ANDA (Abbreviated New Drug Application) |
| Purpose | Approval for entirely new, innovative drugs | Approval for generic versions of existing brand-name drugs |
| Clinical Trial Data | Extensive clinical trials required to establish safety & efficacy for the first time | Relies on existing clinical data for the reference listed drug (RLD) |
| Focus | Demonstrating safety & efficacy of a novel drug | Demonstrating bioequivalence to a previously approved RLD |
Which Regulatory Authorities are Involved in ANDA submission approvals?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States plays a central role in reviewing and approving ANDA submissions. For more information on ANDA on the FDA’s website, please visit this piece of information. Other regulatory authorities may be involved depending on the country or region.
Key Components of an ANDA Submission Package
A complete ANDA submission package comprises several critical components, as outlined in the table below:
| Component | Description |
| Cover Letter | A brief overview of the submission and relevant information such as the applicant’s contact details. |
| Table of Contents | A detailed outline of the contents within the ANDA submission package. |
| Application Form (FDA 356h) | A standardized form provided by the FDA that collects information about the applicant, the drug product, and other details. |
| Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) Information | Detailed information about the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), the finished dosage form, manufacturing processes, quality control measures, specifications, stability data, and analytical methods. |
| Labeling | Proposed labeling for the generic drug product, including package insert, patient information leaflet, and carton/container labeling. |
| Bioequivalence Data | Data from in vivo or in vitro studies demonstrating the generic drug’s bioequivalence to the reference listed drug (RLD). |
| Clinical Data (if applicable) | Clinical data may be required for complex generic drugs or those with special considerations. |
| Administrative Information | Application number, user fees, patent certification and exclusivity information, and other administrative details. |
| Certification and Declaration | Certifications and declarations regarding patent information, active ingredients, and bioequivalence. |
| Facility Information | Details about manufacturing, packaging, testing, and storage facilities involved in producing the generic drug product. |
| Environmental Assessment (if applicable) | An assessment may be required for drug products with potentially significant environmental impacts. |
| Payment Information | Payment of applicable user fees for the ANDA submission. |
Importance of Proper ANDA Submissions
A well-prepared ANDA submission package is crucial for efficient review and approval by regulatory authorities. Just like in any other regulatory submission, thorough and accurate documentation ensures:
- Smooth and timely processing of the application
- Clear demonstration of the generic drug’s safety, efficacy, and bioequivalence
- Compliance with regulatory requirements
- Increased success rate for ANDA approval
Guidance for ANDA Submissions
The ANDA submission process requires careful preparation and adherence to regulatory guidelines. But, how can you ensure a smooth ANDA application process?
Here’s a breakdown of some key aspects to ensure compliance.
Preparing a Well-Organized ANDA Package:
- Assemble a comprehensive ANDA package that adheres to the latest FDA guidelines. The FDA provides detailed guidance documents outlining the specific requirements for each section of the ANDA submission. Carefully review these documents to ensure your application includes all the necessary information presented in a clear, concise, and well-organized manner. You can also check out this article by the FDA Group on compiling an ANDA submission package.
ANDA Submission Process
Just like any other regulatory submission, the ANDA submission process follows a defined pathway with several key stages:
Pre-submission Planning and Preparation:
- Thorough review of the reference listed drug (RLD): This initial step involves meticulously studying the RLD, including its chemical composition, manufacturing process, labeling, and any relevant patents. This understanding forms the foundation for developing your generic drug and demonstrating its bioequivalence to the RLD.
- Development of the generic drug formulation: Based on the RLD information, scientists formulate the generic drug, ensuring it matches the RLD’s characteristics in terms of active ingredients, dosage form, and strength.
- Conducting bioequivalence studies: These studies, as mentioned earlier, are crucial for demonstrating that the generic drug delivers the medication to the bloodstream in a way comparable to the RLD; and opens a path to having your ANDA submission approved.
Compilation of Required Documentation:
- Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) Information: This comprehensive section details the generic drug’s composition, manufacturing processes, quality control procedures, and stability data.
- Bioequivalence Study Data: The data from your bioequivalence studies demonstrating bioequivalence to the RLD is compiled and included in the submission package.
- Labeling: Proposed labeling for the generic drug product, including the package insert and patient information, is prepared according to regulatory requirements.
- Other Supporting Documentation: This may include patent certification information, facility details, and environmental assessments (if applicable).
Submission Timeline and Deadlines:
- Assemble a well-organized ANDA package meeting all FDA requirements.
- Submit the complete electronic application through the FDA’s designated electronic submission platforms. Following submission, the FDA assigns an application number for tracking purposes.
- The review process can take up to several months. Be prepared. The efficacy and the safety of the drug must be thoroughly evaluated by the FDA. The ANDA submissions, and the review timeline, can vary depending on the complexity of the generic drug. Please see Federal Register’s website on the ANDA approval timelines.
Interaction with Regulatory Agencies During the Review Process:
- Maintain open communication with the FDA throughout the review process. The FDA may have questions or require additional information from the applicant. Your quick and clear responses will only help the FDA speed up the review process.
Have you received queries regarding the ANDA submission package from the FDA?
Carefully address any questions or requests for additional information. The FDA may require clarification on specific aspects of the ANDA submission or request further data. Provide thorough and timely responses to ensure a smooth review process. This process, just like any other regulatory submission process, typically requires involving subject-matter experts to give the best possible answers.
How can you prepare a well-organized, compliant ANDA package?
- Partner with companies that have experience in ANDA submissions. The submission process can be complex, and consulting with experienced professionals can be invaluable. They can provide guidance on navigating the complex regulatory landscape, ensuring your application meets all the requirements, and addressing any potential hurdles.
- Maintain a robust Quality Management System (QMS) throughout manufacturing. A strong QMS ensures consistent quality throughout the manufacturing process, from obtaining raw materials to producing the finished drug product. This focus on quality is paramount for demonstrating compliance with FDA regulations and producing a safe and effective generic drug.
Conducting Bioequivalence Studies and Demonstrating Therapeutic Equivalence:
- Design bioequivalence studies that are statistically sound and meet regulatory requirements. Bioequivalence studies are a critical component of an ANDA submission, as they demonstrate that the generic drug delivers the same amount of medication to the bloodstream in the same way as the reference listed drug (RLD). Carefully design these studies following FDA guidelines to ensure they provide robust data supporting bioequivalence.
- Consider therapeutic equivalence for complex generic drugs. In some cases, particularly for complex generic drugs or those with unique delivery mechanisms, demonstrating therapeutic equivalence may be required. Therapeutic equivalence goes beyond bioequivalence and indicates that the generic drug produces the same clinical effect as the RLD. Work closely with the FDA to determine if therapeutic equivalence studies are necessary for your specific ANDA submission. In some cases, this may not be required.
Utilizing Electronic Submission Platforms and Data Standardization:
- The FDA has established electronic submission platforms to facilitate efficient application processing. Utilize the FDA’s electronic submission platforms for streamlined ANDA filings.
- Standardize data formats for consistent and efficient processing. Regulatory agencies often require specific data formats for ANDA submissions. Implementing standardized data formats across your organization ensures consistency and accuracy within your application package, minimizing the risk of errors or delays during processing.
Incorporating Feedback from Reference Drug Labeling and Regulatory Guidance:
- Review the reference listed drug (RLD) labeling thoroughly and address any discrepancies in your proposed labeling. The RLD labeling serves as a reference point for your generic drug’s labeling. Meticulously review the RLD labeling to ensure your proposed labeling accurately reflects the information on the brand-name drug, addressing any discrepancies and providing clear and consistent information for healthcare professionals and patients.
- Stay current on relevant regulatory guidance documents and incorporate that information into your ANDA submission. The FDA and other regulatory authorities frequently issue guidance documents that clarify or update specific ANDA requirements. Regularly monitor for new guidance documents and incorporate this information into your ANDA package to ensure it aligns with the most recent regulatory expectations. One place to stay up to date on Regulatory news and updates is our Accelerating eCTD Submissions LinkedIn Newsletter.
By following these guidelines and maintaining open communication with the regulatory authority throughout the process, you can significantly increase your chances of a successful ANDA submission and expedite the availability of your generic drug to patients.
What are the requirements for ANDA submissions?
Successfully navigating the ANDA submission process requires meeting specific legal, regulatory, and technical requirements established by regulatory authorities like the FDA. Let’s have a look at the specific requirements:
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
- Patent Landscape: ANDA submissions must address any patent exclusivity periods that may still be in effect for the reference listed drug (RLD). This may involve submitting patent certification statements outlining potential patent infringement or seeking legal pathways to market the generic drug after patent expiration has occurred. Regulatory exclusivity periods may also exist for certain types of data associated with the RLD. ANDA applicants need to be aware of these exclusions and ensure their submissions comply with the relevant data exclusivity timelines.
- Labeling Requirements: Generic drug labeling is subject to strict regulations, ensuring accurate and consistent information is conveyed to healthcare professionals and patients. This includes details on the drug’s composition, indications for use, dosage, contraindications, and potential side effects. The FDA provides specific labeling guidelines that ANDA applicants must follow to ensure their labeling is compliant.
Documentation Standards and Formatting
- Electronic Submissions: The FDA mandates that ANDA submissions be filed electronically through designated platforms. Applicants must ensure their submissions comply with the specific electronic format requirements established by the FDA. Please take a look at our FDA PDF specifications checklist for more information.
- Standardized Data Formats: Regulatory agencies often require specific data formats for ANDA submissions. Implementing standardized data formats across your organization ensures consistency and accuracy within your application package, minimizing the risk of errors or delays during processing.
- Clear and Concise Communication: The ANDA documentation should be well-organized, with clear and concise language. This facilitates efficient review by regulatory authorities and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings or requests for clarification.
Demonstrating Bioequivalence, Safety, Efficacy, and Quality
- Bioequivalence Studies: As a cornerstone of ANDA submissions, bioequivalence studies demonstrate that the generic drug delivers the same amount of medication to the bloodstream in the same way as the RLD. These studies play a critical role in establishing the therapeutic equivalence of the generic drug.
- Safety and Efficacy Data: While ANDAs don’t require extensive clinical trials like NDAs (New Drug Applications) for entirely new drugs, safety, and efficacy data may be necessary for complex generic drugs or those with unique delivery mechanisms. The FDA will determine if such data is required on a case-by-case basis.
- Quality Control Measures: A robust Quality Management System (QMS) ensures consistent quality throughout the manufacturing process of the generic drug. This includes meticulous documentation of manufacturing procedures, quality control checks at every stage, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Drug Master Files (DMFs)
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Manufacturers of generic drugs must comply with established GMP regulations to ensure the quality and safety of their products.These regulations outline stringent standards for manufacturing processes, facilities, personnel qualifications, and quality control procedures. Following GMP regulations is crucial for demonstrating that the generic drug meets the same quality standards as the RLD.
- Drug Master Files (DMFs): DMFs are electronic submissions containing detailed information about the safety and manufacturing of drug substances and excipients. Applicants may reference relevant DMFs previously submitted to the FDA to avoid duplicating information within their ANDA package. This can streamline the submission process by leveraging existing data on file with the regulatory agency.
What common challenges can you expect for your ANDA submission?
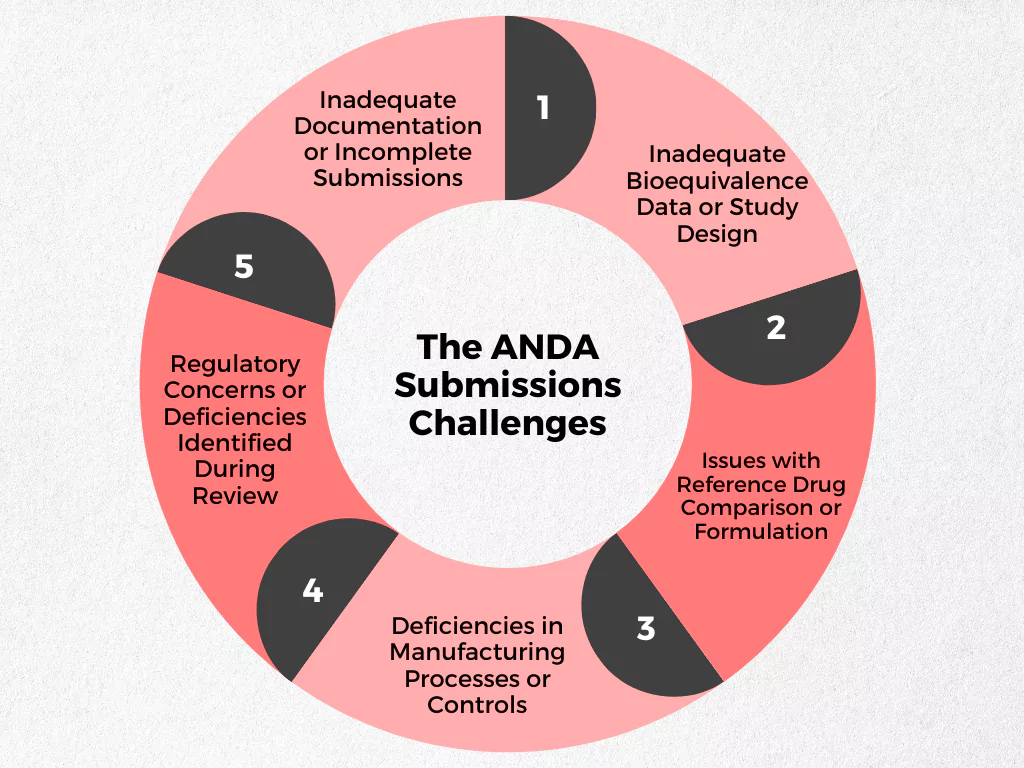
Navigating the ANDA submission process can be complex, and even experienced companies may encounter hurdles along the way. What are some of the most frequent challenges, though?
- Inadequate Bioequivalence Data or Study Design: Demonstrating bioequivalence is a critical element of an ANDA submission. However, poorly designed studies or insufficient data can lead to application rejections. This can involve issues with sample size, statistical analysis, or deviations from established protocols during the bioequivalence studies.
- Issues with Reference Drug Comparison or Formulation: Accurately characterizing the reference listed drug (RLD) and developing a generic version with a bioequivalent formulation are essential. Challenges can arise in obtaining a reliable source of the RLD, accurately replicating its complex formulations, or ensuring the generic drug’s stability throughout its shelf life.
- Deficiencies in Manufacturing Processes or Controls: A robust and compliant manufacturing process is vital for producing safe and effective generic drugs. However, deficiencies in manufacturing practices, inadequate quality control measures, or deviations from established protocols can raise red flags during the FDA review process.
- Regulatory Concerns or Deficiencies Identified During Review: The FDA meticulously reviews ANDA submissions. Regulatory concerns may arise if the application lacks clarity, contains inconsistencies, or fails to meet current regulatory expectations. These concerns can lead to requests for additional information or delays in the approval process.
- Inadequate Documentation or Incomplete Submissions: A well-organized and complete ANDA submission package (just like any other regulatory submission) is crucial for efficient review. Incomplete documentation, missing data, or unclear information can lead to delays or rejections. This can include issues with formatting, data standardization, or adherence to labeling requirements.
How DocShifter Can Help
Just like with any other regulatory submission, it is crucial to adhere to specific document regulations for your ANDA submission. As a document conversion/validation solution for the regulated enterprise, DocShifter software ensures that all your documents are fully technically compliant with the FDA’s specifications.
From the right navigation elements to the compliant PDF specifications, DocShifter automates all your compliant document preparation process in one go.
By understanding these common challenges and leveraging available resources, companies can increase their chances of a successful ANDA submission and expedite the process of bringing safe and affordable generic drugs to market.
Conclusion
The ANDA submission process plays a critical role in ensuring the timely availability of safe and affordable generic medications. By following best practices and adhering to regulatory requirements, companies can navigate this process effectively and contribute to a more accessible healthcare landscape. And of course, more affordable medications for the public, too. After all, people come first!
Recap: The Significance of ANDA Submissions
Proper ANDA submissions are instrumental in:
- Expanding Access to Affordable Medications: Generic drugs offer patients significant cost savings compared to brand-name drugs, allowing for wider access to essential treatments for a larger population. This is particularly crucial for patients with chronic conditions requiring ongoing medication use.
- Fostering Competition in the Pharmaceutical Market: ANDA submissions pave the way for competition by allowing multiple manufacturers to produce generic versions of brand-name drugs after patent expiration. This competition can drive down drug prices and incentivize continued innovation in generic drug development.
- Ensuring Safety, Efficacy, and Quality of Generic Drugs: The rigorous ANDA review process by regulatory authorities like the FDA guarantees that generic drugs meet the same safety and efficacy standards as their brand-name counterparts. Patients can be confident that generic medications are effective and will produce the intended therapeutic results.
Key Considerations for Successful ANDA Submissions
Even though we mentioned these in our blog above, let’s repeat once more the key considerations for a successful ANDA submission.
- Thorough understanding of the reference listed drug (RLD)
- Well-designed bioequivalence studies demonstrating bioequivalence
- Adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and quality control measures
- Clear and concise communication within the ANDA documentation package
- Compliance with all regulatory requirements and formatting guidelines for each document that goes into the ANDA submission
- Open communication and prompt responses to inquiries from regulatory agencies