Biologics License Application (BLA) Guide
-
By DocShifter
- 12 minutes read
The application tells the health authority all about the medicine, how it’s made, and how safe and effective it is based on scientific studies. The health authority then carefully reviews everything to make sure the medicine is good for patients before they say yes. This process helps keep people safe and healthy. For more information about regulatory submissions in general, please review this regulatory submissions guide.
In this guide, you will find a comprehensive roadmap to navigating the BLA submission process, from understanding the importance of BLAs for bringing innovative treatments to patients to successfully obtaining approval from health authorities. We’ll break down the key steps involved, common challenges to anticipate, and valuable strategies to expedite your application process.
Understanding BLA Submissions in More Detail
BLAs are typically submitted to regulatory agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States or the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe. These agencies play a vital role in safeguarding public health by ensuring the safety and effectiveness of biological products. In other words, based on (tremendous) amount of data, these agencies decide whether the developed formulas are safe for public consumption or not.
The responsibility for submitting a BLA falls on the shoulders of any legal entity taking ownership of the product’s development and commercialization. This could be a pharmaceutical company, a research institution, or even a contract manufacturing organization (CMO) depending on the specific product and development pathway.
Be careful though; BLA submissions are mandatory when a company seeks marketing authorization for a novel biological product. This typically occurs after successful completion of clinical trials demonstrating the product’s safety and efficacy in treating a specific disease or condition.
BLA Submission Process
Like any other regulatory submission type, the BLA submission process is a meticulous and multi-layered journey that ensures the safety and efficacy of biological products before they reach patients. This process safeguards public health by rigorously evaluating the product’s characteristics, potential benefits, and any associated risks. What are the stages involved in a typical BLA submission?
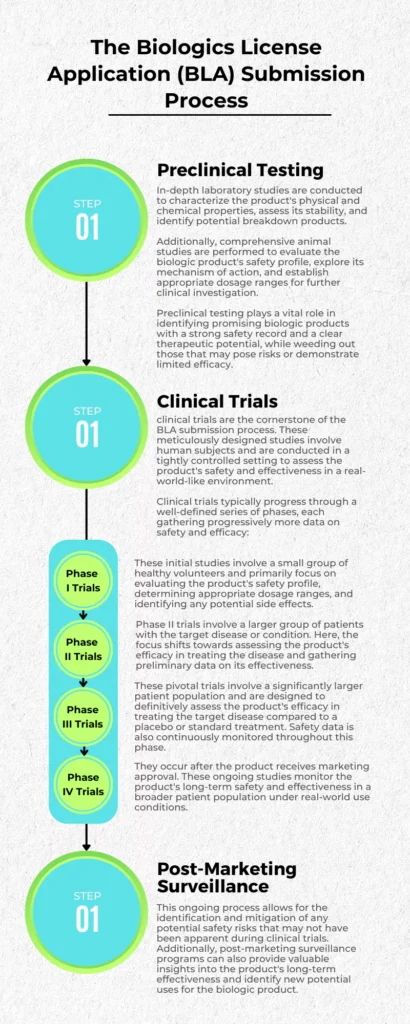
Preclinical Testing
This foundational phase lays the groundwork for clinical trials. In-depth laboratory studies are conducted to characterize the product’s physical and chemical properties, assess its stability, and identify potential breakdown products. Additionally, comprehensive animal studies are performed to evaluate the biologic product’s safety profile, explore its mechanism of action, and establish appropriate dosage ranges for further clinical investigation.
Preclinical testing plays a vital role in identifying promising biologic products with a strong safety record and a clear therapeutic potential, while weeding out those that may pose risks or demonstrate limited efficacy.
Clinical Trials
Building upon the groundwork laid by preclinical testing, clinical trials are the cornerstone of the BLA submission process. These meticulously designed studies involve human subjects and are conducted in a tightly controlled setting to assess the product’s safety and effectiveness in a real-world-like environment.
Clinical trials typically progress through a well-defined series of phases, each gathering progressively more data on safety and efficacy:
- Phase I Trials: These initial studies involve a small group of healthy volunteers and primarily focus on evaluating the product’s safety profile, determining appropriate dosage ranges, and identifying any potential side effects.
- Phase II Trials: Expanding on the findings from Phase I, Phase II trials involve a larger group of patients with the target disease or condition. Here, the focus shifts towards assessing the product’s efficacy in treating the disease and gathering preliminary data on its effectiveness.
- Phase III Trials: These pivotal trials involve a significantly larger patient population and are designed to definitively assess the product’s efficacy in treating the target disease compared to a placebo or standard treatment. Safety data is also continuously monitored throughout this phase.
- Phase IV Trials: Also known as post-marketing surveillance studies, Phase IV trials occur after the product receives marketing approval. These ongoing studies monitor the product’s long-term safety and effectiveness in a broader patient population under real-world use conditions.
Post-Marketing Surveillance
Even after receiving marketing authorization, the responsibility for ensuring a product’s safety and efficacy doesn’t cease. Manufacturers are required to implement robust post-marketing surveillance programs to continuously monitor the product’s performance in the real world. This ongoing process allows for the identification and mitigation of any potential safety risks that may not have been apparent during clinical trials. Additionally, post-marketing surveillance programs can also provide valuable insights into the product’s long-term effectiveness and identify new potential uses for the biologic product.
What to Include in Your BLA Submission Package
We know what the BLA submission process more or less looks like by now. How about going through with a BLA submission? What do you need to include?
Here’s a breakdown of the key components you’ll need to include:
- Applicant Information: This section establishes your credentials and role in bringing the biologic product to market. It should provide details such as the applicant’s legal name and address, contact information for key personnel, and a clear outline of your responsibility for the product’s development and commercialization.
- Product/Manufacturing Information: This section dives deep into the specifics of your biologic product and its manufacturing process. Here, you’ll provide a comprehensive description of the product, including its source material, structure, and function. Additionally, detailed information on the manufacturing process, quality control procedures, and facility specifications will be required. This section assures the regulatory agency that the product is manufactured consistently and meets stringent quality standards.
- Pre-clinical Studies: The data gathered from your preclinical testing program plays a critical role in establishing the foundation for your BLA submission. This section should provide a comprehensive overview of the studies conducted, including methodologies, results, and a clear interpretation of the findings. Data on the product’s safety profile, stability, and potential efficacy should be meticulously documented.
- Clinical Studies: This section forms the heart of your BLA submission and showcases the data gathered from your clinical trials program. Detailed reports for each phase of the clinical trials, including Phase I, II, III, and any post-marketing surveillance studies, need to be included. These reports should encompass study design, methodology, patient demographics, results, and a statistical analysis of the data. The focus here is to demonstrate the product’s safety and efficacy in a well-defined and controlled setting.
- Labeling: The proposed product labeling is an essential component of your BLA submission. This document serves as the official product information for healthcare professionals and patients. A well-designed label clearly outlines the product’s indications for use, dosage and administration instructions, potential side effects, and any relevant warnings or precautions. The labeling must comply with regulatory requirements and ensure clear and accurate communication about the product’s use.
The BLA submission Review Process
While the specifics of the BLA review process may differ slightly between Health Authorities (HAs) around the world, the core principles remain consistent – ensuring the product’s safety, efficacy, and quality.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the typical review process with a focus on the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, given the wealth of available information.
For a comprehensive look at the review processes of various HAs, please refer to the following table:
| Health Authority | BLA Review Process Information |
| European Medicines Agency (EMA) | https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/marketing-authorisation |
| Health Canada | https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/drug-products/applications-submissions/guidance-documents.html |
| China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) | https://english.nmpa.gov.cn/ (Chinese language only) |
| Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) of Japan | https://www.pmda.go.jp/english/ (Japanese language only) |
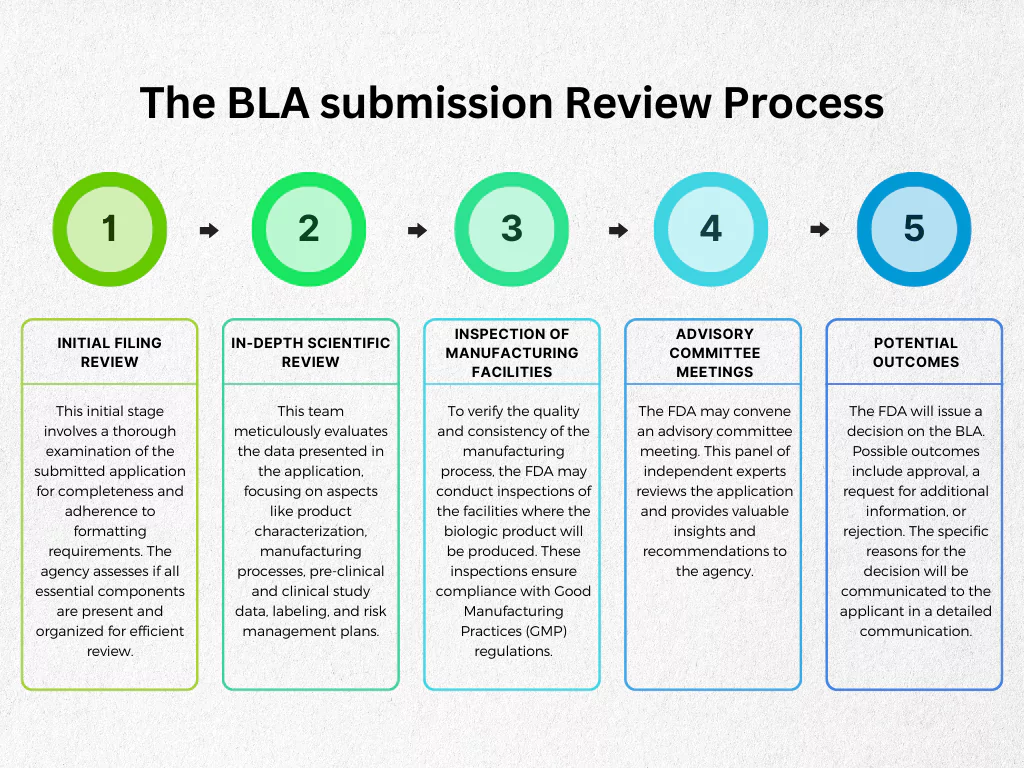
Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved in the FDA’s BLA review process:
- Initial Filing Review: This initial stage involves a thorough examination of the submitted application for completeness and adherence to formatting requirements. The agency assesses if all essential components are present and organized for efficient review.
- In-depth Scientific Review: Once the initial filing hurdle is cleared, the BLA undergoes a meticulous scientific review by a dedicated team of reviewers. This team meticulously evaluates the data presented in the application, focusing on aspects like product characterization, manufacturing processes, pre-clinical and clinical study data, labeling, and risk management plans. The reviewers meticulously analyze the data to ensure the product’s safety and efficacy are adequately supported by scientific evidence.
- Inspection of Manufacturing Facilities: To verify the quality and consistency of the manufacturing process, the FDA may conduct inspections of the facilities where the biologic product will be produced. These inspections ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations.
- Advisory Committee Meetings: For particularly complex BLAs or those involving novel therapeutic approaches, the FDA may convene an advisory committee meeting. This panel of independent experts reviews the application and provides valuable insights and recommendations to the agency.
- Potential Outcomes: Following a comprehensive review, the FDA will issue a decision on the BLA. Possible outcomes include approval, a request for additional information, or rejection. The specific reasons for the decision will be communicated to the applicant in a detailed communication.
Understanding the review process timeline is crucial. While the FDA strives to complete BLA reviews within a specific timeframe, the complexity of the product and the completeness of the application can significantly influence the review duration.
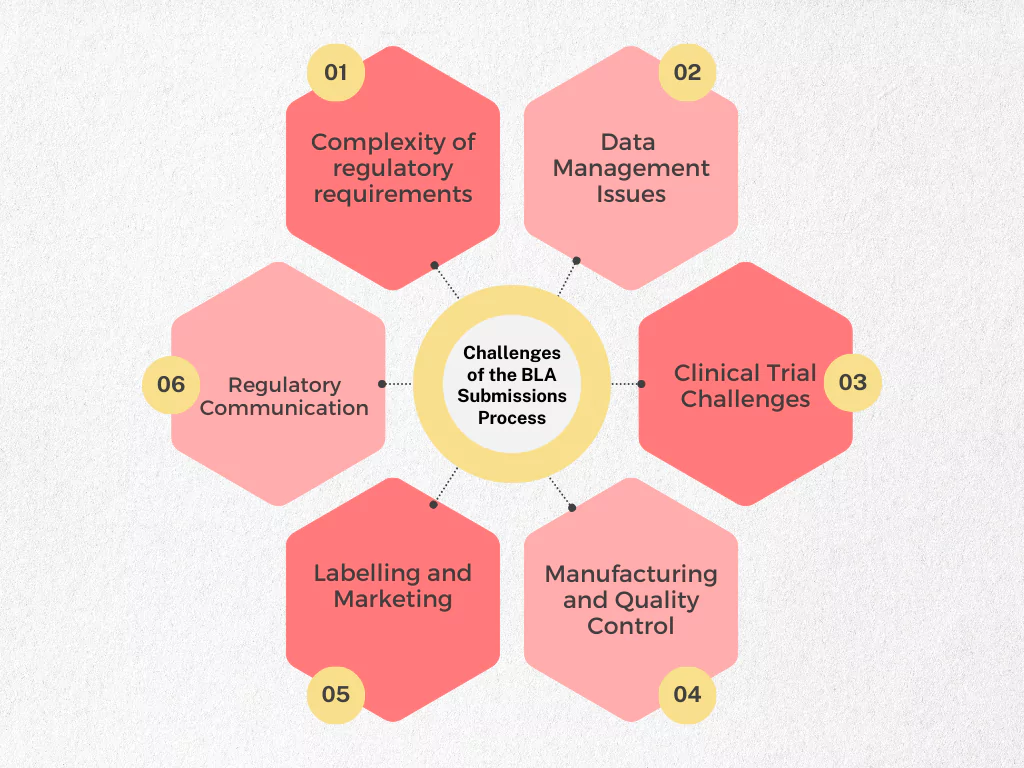
Navigating the BLA submission process requires meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive understanding of regulatory requirements. Here are some common challenges and pitfalls to be aware of:
Complexity of Regulatory Requirements
Health Authorities (HAs) have stringent guidelines for BLA submissions. These guidelines encompass everything from completeness and accuracy of data to formatting and presentation. Failing to meet these requirements can lead to delays, requests for additional information (RFAIs), or even rejection of the application.
Data Management Issues
BLAs involve a massive volume of complex data from preclinical studies, clinical trials, and manufacturing processes. Managing this data effectively, ensuring its integrity, and presenting it in a clear and concise manner is crucial. Inconsistencies or inaccuracies in data can raise red flags for reviewers and cast doubt on the product’s safety and efficacy.
Clinical Trial Challenges
The success of a BLA submission hinges on robust clinical trial data. Challenges like enrolling sufficient patients, ensuring patient compliance, and managing unforeseen safety issues during trials can significantly impact the timeline and overall strength of the application.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
BLAs require detailed information on the manufacturing process and robust quality control procedures.Inconsistencies in manufacturing or deviations from established quality control protocols can raise concerns about the product’s consistency and safety profile.
Labeling and Marketing
The product labeling plays a vital role in ensuring safe and effective use of the biologic product. Developing clear, concise, and compliant labeling that accurately reflects the product’s benefits and risks is essential. Additionally, marketing materials must adhere to strict regulations to avoid misleading claims.
Regulatory Communication
Effective and timely communication with HAs is paramount throughout the BLA review process. Prompt responses to inquiries, clear explanations of any data discrepancies, and proactive engagement with the agency can significantly influence the review timeline and outcome.
How to overcome common challenges related to BLA submissions
A well-defined strategy and the right tools can help mitigate these challenges and streamline the BLA submission process. Here are some key considerations:
- Experienced Team: Assemble a team with expertise in regulatory affairs, clinical research, and BLA preparation. Their knowledge and experience can ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and facilitate effective communication with HAs.
- Comprehensive Data Management Plan: Develop a robust data management plan to ensure data integrity, consistency, and efficient retrieval. Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems can be invaluable in streamlining data collection and management.
- Quality Management System (QMS): Implement a robust QMS to ensure consistent quality throughout the manufacturing process. Regular audits and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations are essential for building confidence in the product’s safety and quality.
- Regulatory Expertise: Seek guidance from regulatory consultants or partner with a Contract Research Organization (CRO) with extensive experience in BLA submissions. Their expertise can help navigate the complexities of the process and ensure compliance with all relevant guidelines.
Streamlining compliant BLA documentation with DocShifter:
Like with any regulatory submission type, the health authorities demand navigation-rich, text-searchable, submission-ready PDF documents to accelerate the submission review process.
DocShifter, an automated document conversion and validation software, allows the conversion of various digital documents into submission-ready, high quality PDF documents. No matter where your content resides; Veeva, OpenText Documentum, Generis CARA, LORENZ Docubridge, Microsoft SharePoint, Ennov platform.
These are the benefits our customers are seeing by automating compliant document preparation with DocShifter:
Accelerated document preparation = Faster time to market
Streamline and easily ensure submission-readiness for internal and external PDFs
Reduce risk of non-compliance through automation
Move PDF compliance earlier in your submission process,
Speed Up Your BLA Submissions
A successful BLA submission hinges on a meticulous process that ensures the safety and efficacy of your biologic product. However, navigating the complexities of regulatory requirements, data management, and effective communication with Health Authorities (HAs) can add significant time to the process.
Here’s a quick recap of some key strategies to expedite your BLA submission:
- Assemble a Team with Expertise: Build a team with the knowledge and experience to navigate the regulatory landscape and ensure clear communication with HAs.
- Embrace Technology: Utilize electronic data capture (EDC) systems for efficient data management and DocShifter for centralized document storage, version control, automated formatting, and template management. These tools can significantly streamline document preparation and ensure adherence to formatting requirements.
Plan and Communicate Proactively: Develop a comprehensive data management plan and a robust quality management system (QMS) early on. Proactive communication with HAs throughout the process can address any questions or concerns promptly, avoiding delays.
Taking the Next Step
Ready to leverage technology to streamline your IND submissions and accelerate your drug development journey?
- Join our Accelerating eCTD Submissions LinkedIn Newsletter: Connect with a community of pharmaceutical professionals and gain access to valuable insights and free tips on INDs, eCTD submissions and lots of other topics.