FDA eCTD Validation Criteria: A Comprehensive Guide
-
By DocShifter
- 4 minutes read
The electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD) has revolutionized the drug development and approval process. By standardizing the format for regulatory submissions, the eCTD has streamlined interactions between pharmaceutical companies and regulatory authorities like the FDA. However, ensuring compliance with FDA eCTD validation criteria remains a complex challenge for many organizations.
The Importance of eCTD Submissions
The eCTD format is now mandatory for most drug submissions to the FDA. It provides a structured approach to organizing and presenting regulatory information, improving efficiency and transparency. Successful eCTD submissions are crucial for accelerating drug development timelines and increasing the likelihood of regulatory approval.
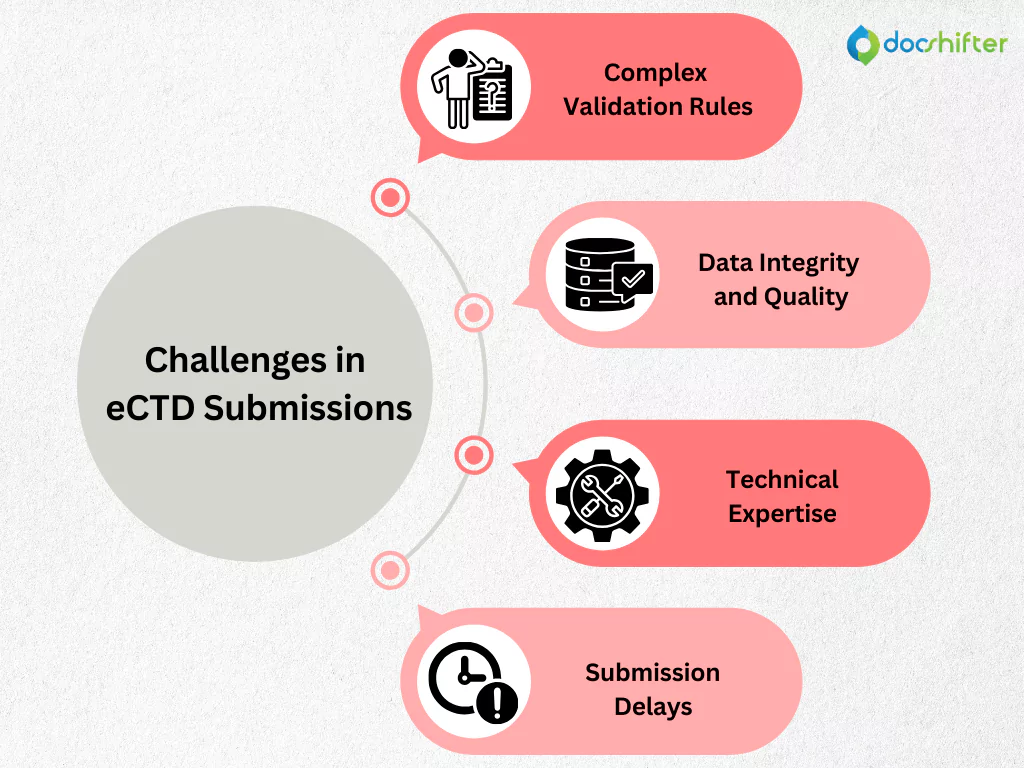
Challenges in eCTD Submissions
Despite its benefits, the eCTD presents several challenges for pharmaceutical companies:
- Complex Validation Rules: The FDA has stringent validation criteria that must be meticulously followed to avoid submission rejections.
- Data Integrity and Quality: Ensuring data accuracy and consistency throughout the eCTD package is essential.
- Technical Expertise: Building and maintaining the necessary technical infrastructure and expertise can be resource-intensive.
- Submission Delays: Errors in validation can lead to significant delays in the drug approval process.
The Scale of the Challenge
By understanding the importance of eCTD submissions, the challenges faced by the industry, and the scale of the issue, we can better appreciate the critical role of validation in achieving regulatory success.
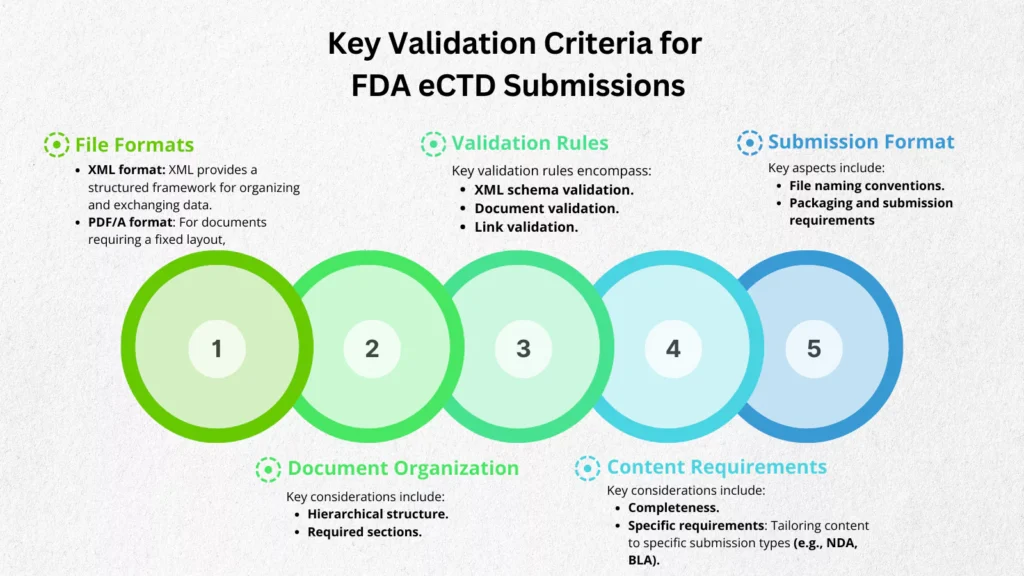
Key Validation Criteria for FDA eCTD Submissions
The FDA has established stringent validation criteria to ensure the quality, integrity, and consistency of eCTD submissions. Adherence to these criteria is crucial for efficient review and regulatory approval.
Please see the official eCTD error codes validation list here in a PDF format: https://www.fda.gov/media/87056/download
Let’s delve into the key validation areas:
File Formats
Correct file formats are foundational for eCTD compliance. The FDA mandates:
- XML format: As the backbone of eCTD, XML provides a structured framework for organizing and exchanging data. Ensuring XML compliance is essential for data integrity and efficient processing.
- PDF/A format: For documents requiring a fixed layout, PDF/A is the preferred format. Adherence to PDF/A standards preserves document integrity and ensures accurate rendering.
Document Organization
A well-structured eCTD facilitates efficient review. Key considerations include:
- Hierarchical structure: Following the eCTD’s hierarchical organization ensures logical information flow and easy navigation.
- Required sections: Adhering to the FDA’s mandated sections and their specified order is crucial for compliance.
Validation Rules
Rigorous validation is essential to identify and rectify errors before submission. Key validation rules encompass:
- XML schema validation: Ensuring strict adherence to the defined XML structure prevents processing errors and guarantees data consistency.
- Document validation: Verifying document formatting, completeness, and accuracy maintains data integrity and enhances review efficiency.
- Link validation: Ensuring all internal and external links function correctly improves navigation and prevents information gaps.
Content Requirements
Comprehensive and accurate content is paramount for regulatory approval. Key considerations include:
- Completeness: Ensuring all required information is included prevents submission deficiencies.
- Specific requirements: Tailoring content to specific submission types (e.g., NDA, BLA) demonstrates a thorough understanding of regulatory expectations.
Submission Format
Proper formatting optimizes submission processing. Key aspects include:
- File naming conventions: Adhering to FDA guidelines for file naming ensures efficient file management and identification.
- Packaging and submission requirements: Complying with FDA submission specifications streamlines the submission process and minimizes errors.
Mastering FDA eCTD validation is essential for pharmaceutical companies seeking efficient regulatory approval. By adhering to strict file formats, meticulous document organization, and comprehensive validation rules, companies can significantly enhance their chances of submission success.
Key takeaways include:
- The importance of XML and PDF/A formats for data integrity.
- The critical role of document structure and content completeness.
- The necessity of robust validation processes to identify and rectify errors.
- The significance of compliance with submission format requirements.
By implementing a comprehensive validation strategy and staying updated with FDA guidelines, pharmaceutical companies can streamline their eCTD submissions, reduce review cycles, and ultimately accelerate drug development timelines.
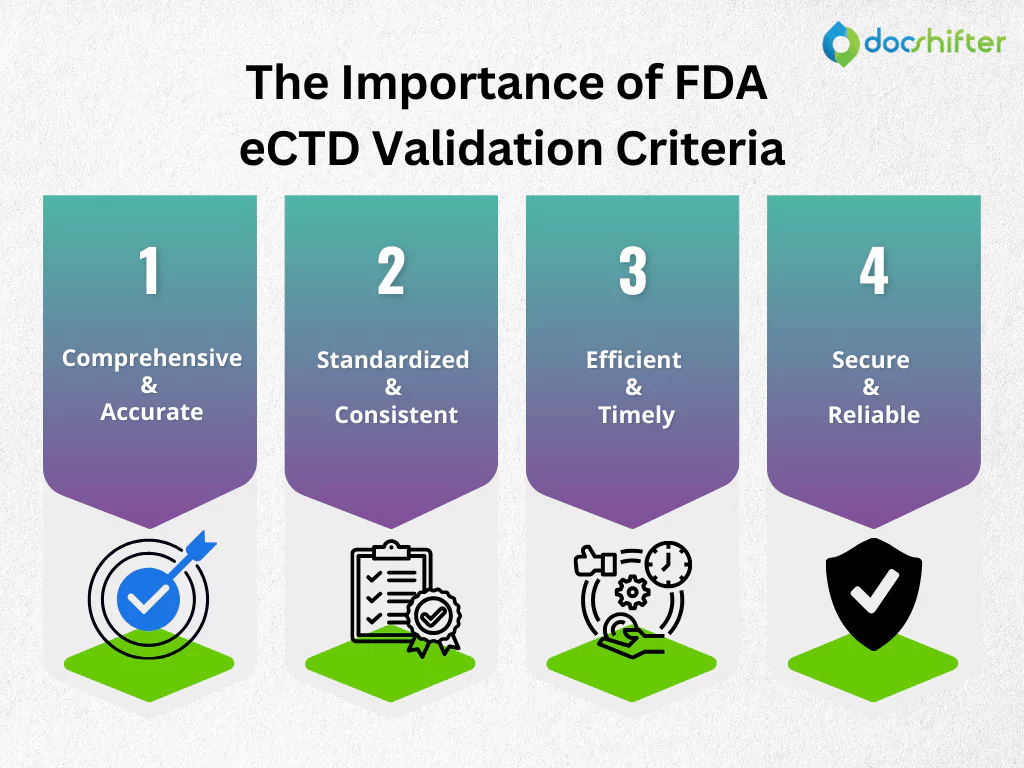
The Importance of FDA eCTD Validation Criteria
FDA eCTD Validation Criteria serve as a cornerstone for ensuring the integrity, consistency, and efficiency of electronic regulatory submissions. By adhering to these criteria, regulatory submissions become more:
- Comprehensive and accurate: The validation process helps identify and rectify errors or omissions in the submitted data, ensuring that all required information is present and correct.
- Standardized and consistent: By following predefined standards, submissions become more uniform, facilitating easier review and comparison by regulatory authorities.
- Efficient and timely: Adherence to validation criteria can expedite the review process, as submissions that meet the standards are less likely to be delayed due to technical issues.
- Secure and reliable: The validation criteria contribute to the security and reliability of submissions, reducing the risk of data corruption or loss during transmission.