What are New Drug Applications? A Complete Guide to NDAs
-
By DocShifter
- 15 minutes read
The answer lies in a document called a New Drug Application (NDA). An NDA is a comprehensive package submitted to regulatory authorities by drug developers. It essentially tells the full story of a new drug, detailing years of research, laboratory testing, human trials, and manufacturing information. And this article will give you everything you need to know about New Drug Applications.
Table of Contents
1. What are New Drug Applications?
2. Why are NDAs Important?
3. What Information is included in an NDA?
4. Importance of NDA Submissions in Pharmaceutical Development
5. Regulatory Bodies Involved in NDA Approvals
6. Key Components of an NDA Submission Package
7. Importance of Proper NDA Submissions
8. Guidance for NDA Submissions
9. NDA Submission Process
10. Pre-submission Planning and Preparation
11. Common Challenges of NDA Submissions
What are New Drug Applications?
An NDA, or New Drug Application, is a comprehensive submission package submitted to regulatory authorities by pharmaceutical companies seeking approval to market a new drug. The NDA includes extensive data on the drug’s safety, efficacy, and manufacturing processes. This data is meticulously reviewed by regulatory bodies to ensure the drug meets strict standards for public safety and effectiveness.
The NDA submission process is complex and demanding, requiring extensive preparation and adherence to regulatory guidelines. Once submitted, the application undergoes a thorough review, which can take several months or even years. During this time, regulatory agencies may request additional information or clarification, and the applicant must respond promptly and comprehensively.
If the NDA is approved, the drug can be commercially available in the designated market. However, the approval process doesn’t end there. Regulatory agencies often conduct ongoing monitoring and surveillance of approved drugs to ensure their continued safety and effectiveness.
This guide will equip you with a comprehensive understanding of NDAs. We’ll break down the different types of NDAs, explore the information typically included, and guide you through the general NDA submission process. You will walk away with insights, and useful links to better understand the whole NDA submission process.
At the end of the article, you will also find a link to our Regulatory Professionals Community on LinkedIn. Give it a like to receive monthly tips & tricks to help accelerate your submissions.
Why are NDAs Important?
NDAs play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and drug effectiveness. We discussed before that a regulatory submission is like the identification of any medicinal product; telling its story from creation to side effects. From A to Z. NDA, plays the same role for new medicines that are planned to be marketed for the very first time.
By thoroughly reviewing the information in an NDA, regulatory authorities assess the potential benefits and risks of a new drug before it’s available for public use.
What Information is included in an NDA?
Think of an NDA as a detailed report card for a new drug. It has to tell everything about it. From the dosage, to the formula development, to the clinical trials, side effects; everything.
An NDA typically contains (but is absolutely not limited to the information below):
- Chemical and pharmacological properties of the drug: This explains how the drug is made and how it’s supposed to work in the body.
- Results of pre-clinical (animal) and clinical (human) trials: This data demonstrates the drug’s safety and effectiveness.
- Manufacturing information: This details the processes and quality control measures in place to ensure consistent production of a safe and effective drug.
- Proposed labeling: This outlines the drug’s intended uses, dosage instructions, potential side effects, and other important information for healthcare professionals and patients. A prescription that typically comes with a prescription medicine, as we know it, is part of this section.
The specific process for submitting an NDA can vary depending on the regulatory authority involved. However, there are generally some common steps, such as compiling data, submitting the application, and undergoing a review process.
We’ll have a look at these steps, as well as potential challenges you can expect when submitting an NDA later on in this guide.
Importance of NDA Submissions in Pharmaceutical Development
NDAs are the cornerstone of bringing safe and effective new drugs to market. In other words, if a new drug is being marketed for the very first time, an NDA submission is required.
Depending on where the drug will be marketed, an NDA needs to be submitted to the respective health authority of that region. For example, the New Drug Application (NDA) has been the cornerstone of ensuring safe and effective medications reach American patients for over eight decades. Since 1938, every new drug has undergone a rigorous NDA review process before hitting pharmacy shelves in the US. This in-depth evaluation by the FDA plays a vital role in protecting public health in the US.
Here’s why NDA submissions are crucial
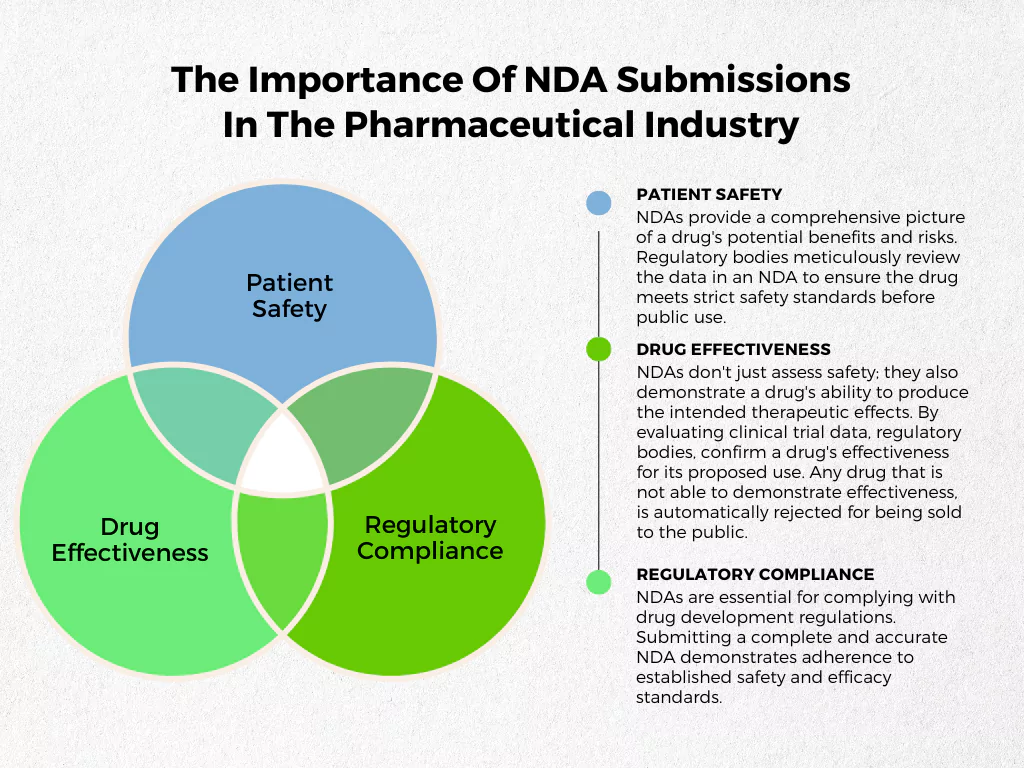
- Patient Safety: NDAs provide a comprehensive picture of a drug’s potential benefits and risks. Regulatory bodies meticulously review the data in an NDA to ensure the drug meets strict safety standards before public use.
- Drug Effectiveness: NDAs don’t just assess safety; they also demonstrate a drug’s ability to produce the intended therapeutic effects. By evaluating clinical trial data, regulatory bodies, confirm a drug’s effectiveness for its proposed use. Any drug that is not able to demonstrate effectiveness, is automatically rejected for being sold to the public.
- Regulatory Compliance: NDAs are essential for complying with drug development regulations. Submitting a complete and accurate NDA demonstrates adherence to established safety and efficacy standards.
Regulatory Bodies Involved in NDA Approvals
The specific regulatory body involved in NDA approval depends on the country where the drug is being developed. Here’s a table outlining some key examples:
| Country | Health Authority | Website | Review Process Link |
| USA | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) | https://www.fda.gov/ | https://www.fda.gov/ |
| European Union (EU) | European Medicines Agency (EMA) | https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/homepage | https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/about-us/what-we-do/authorisation-medicines |
| Japan | Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) | https://www.pmda.go.jp/english/ | https://www.pmda.go.jp/english/about-pmda/0004.html |
Key Components of an NDA Submission Package
An NDA submission package is a compilation of comprehensive documents outlining all aspects of a new drug. Here’s a breakdown of some key components, presented in a table for better readability:
| Component | Description |
| Administrative Information | Formal documents introducing the submission, including a cover letter, application form, and relevant communication with regulatory bodies. |
| Table of Contents (TOC) | Provides an overview of the entire submission, making it easier for reviewers to navigate. |
| Quality Overall Summary (Module 2) | Summarizes the manufacturing processes, controls, and specifications for the drug product. |
| Nonclinical Study Reports (Module 4) | Reports on animal studies evaluating the drug’s pharmacology, toxicology, and other relevant safety aspects. |
| Clinical Study Reports (Module 5) | Detailed reports of clinical trials investigating the drug’s safety and efficacy in humans. |
| Module 1 Documents | Region-specific administrative documents required by the regulatory authority, such as product labeling and patient information leaflets. |
| Quality (Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls) Documents (Module 3) | Detailed information about the drug substance and drug product, including manufacturing processes, specifications, and stability data. |
| Clinical Data (Module 5) | Detailed reports of clinical trials, including study protocols, investigator brochures, and clinical study reports. |
| Safety Data (Module 5) | Safety summaries, including summaries of adverse events, risk management plans, and pharmacovigilance data. |
| Benefit-Risk Assessment | Evaluation of the drug’s benefits and risks based on all available data. |
| Regulatory Commitments | Any commitments made by the applicant to address specific regulatory concerns or requirements. |
| Other Supporting Documents | Additional documents such as literature references, validation data, or bridging studies that support the application. |
| Electronic Backbone Files | XML files containing metadata and hyperlinks to facilitate electronic submission review. |
| Validation Documentation | Documentation confirming that the electronic submission complies with regulatory requirements and standards. |
This breakdown provides a high-level overview of the key components in an NDA submission.
Important to note, though, is that the specific requirements may vary depending on the regulatory body involved. We will mainly focus on the FDA in this guide.
Importance of Proper NDA Submissions
While we’ve touched on the importance of NDAs earlier, proper submissions are crucial for several reasons. When we say proper, we mean complete, accurate and compliant submissions.
- Ensuring Drug Safety and Efficacy: A well-prepared NDA provides a clear and comprehensive picture of a drug’s safety profile and potential benefits. Regulatory bodies rely on this information to thoroughly assess whether the drug meets strict standards for patient safety and effectiveness before granting approval.
- Facilitating Regulatory Approval Processes: A complete and accurate NDA submission streamlines the review process for regulatory authorities. Clear organization, adherence to guidelines, and inclusion of all necessary data allows reviewers to efficiently evaluate the drug’s merits.
- Protecting Public Health and Well-Being: Ultimately, proper NDA submissions safeguard public health by ensuring that only safe and effective new drugs reach the market. Incomplete or inaccurate submissions can delay approval or, in worst-case scenarios, lead to the release of unsafe medications.
Guidance for NDA Submissions
Developing a successful NDA submission requires careful planning and adherence to specific guidelines. Here are some general pointers to keep in mind:
- Preparing the NDA Submission Package: This comprehensive document requires meticulous attention to detail. Familiarize yourself with the regulatory body’s specific requirements and structure your submission accordingly. Utilize the “Common Technical Document (CTD)” format, an internationally recognized standard for organizing NDA submissions.
- Meeting Regulatory Requirements and Guidelines: Each regulatory body has established guidelines for NDA submissions. These guidelines outline the specific data and documentation required for a complete application. Carefully study these guidelines and ensure your submission adheres to all relevant criteria.
- Conducting Pre-submission Meetings with Regulatory Agencies: Many regulatory bodies offer pre-submission meeting opportunities. These meetings allow you to discuss your NDA package with reviewers and clarify any potential concerns before formal submission.
- Utilizing Electronic Submission Platforms (if applicable): Many regulatory bodies have transitioned to electronic submission platforms, or also known as gateways. Familiarize yourself with these platforms and ensure your NDA package is formatted correctly for electronic review.
- Incorporating Feedback from Preclinical and Clinical Trials: The data and insights gleaned from preclinical (animal) and clinical (human) trials are invaluable for your NDA submission. Carefully analyze the results from these trials and address any safety or efficacy concerns raised during the research process.
NDA Submission Process
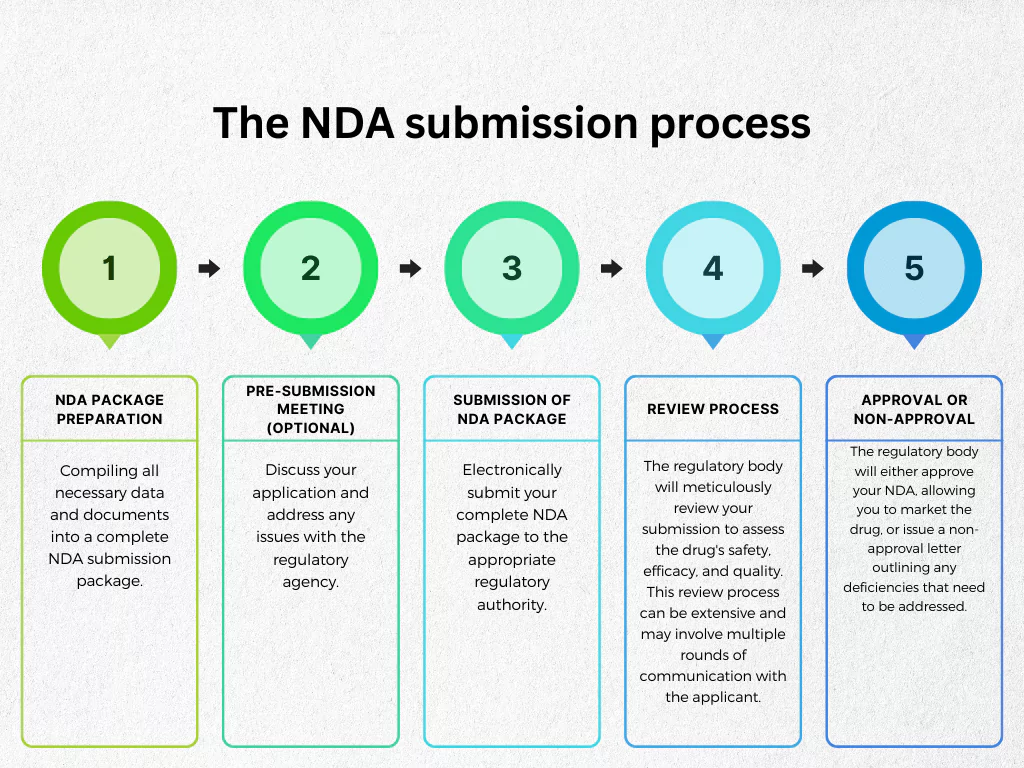
The specific NDA submission process can vary depending on the regulatory body involved. However, here is a 5 step high-level overview of an NDA submission process:
- NDA Package Preparation: Compiling all necessary data and documents into a complete NDA submission package.
- Pre-submission Meeting (Optional): Discuss your application and address any issues with the regulatory agency.
- Submission of NDA Package: Electronically submit your complete NDA package to the appropriate regulatory authority.
- Review Process: The regulatory body will meticulously review your submission to assess the drug’s safety, efficacy, and quality. This review process can be extensive and may involve multiple rounds of communication with the applicant.
- Approval or Non-Approval: Following a thorough review, the regulatory body will either approve your NDA, allowing you to market the drug, or issue a non-approval letter outlining any deficiencies that need to be addressed.
By following these guidelines and understanding the general NDA submission process, you can increase your chances of a successful application and ultimately bring a safe and effective new drug to market.
Now that we’ve covered the general importance and guidance for NDA submissions, let’s delve deeper into the specific stages involved:
Pre-submission Planning and Preparation
This initial phase is crucial for laying the groundwork for a smooth NDA submission process. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Assemble a Team: Building a qualified team with expertise in regulatory affairs, clinical research, and drug development is essential.
- Develop a Submission Strategy: Create a clear roadmap outlining the content of your NDA package, submission timeline, and communication plan with regulatory agencies.
- Familiarize Yourself with Regulatory Requirements: Thorough research of the specific requirements for the target regulatory body is vital.
Compilation of Required Documentation
An NDA submission package is a comprehensive document containing a wealth of information. Here are some core components you’ll need to compile:
- Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) Data: This detailed information outlines the drug substance and drug product, including manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and stability data.
- Clinical Trial Results: This section presents a comprehensive analysis of the data collected during preclinical (animal) and clinical (human) trials. The data should demonstrate the drug’s safety, efficacy, and potential side effects.
- Nonclinical Study Reports: These reports detail studies conducted on animals to assess the drug’s pharmacology, toxicology, and other safety aspects.
- Labeling: Proposed labeling for the drug, including information on its uses, dosage, potential side effects, and contraindications.
Please note: This is not an exhaustive list, and specific requirements may vary depending on the regulatory body. You can use the table above to find out more about the specifications of the region you are submitting to.
Submission Timeline and Deadlines
Deadlines for NDA submissions can vary significantly depending on the chosen regulatory authority.
Here are some examples:
- USA Food and Drug Administration (FDA): https://www.fda.gov/drugs/types-applications/new-drug-application-nda
- European Medicines Agency (EMA): https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/marketing-authorisation/obtaining-eu-marketing-authorisation-step-step
- PMDA in Japan: https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000163784.pdf
Responding to Regulatory Queries and Requests for Additional Information (RQAIs)
Regulatory agencies may issue Requests for Additional Information (RQAIs) during the review process. This type of information is typically requested to clarify things, or in cases where information is lacking in the initial submission package.
These requests may involve clarifying data, addressing specific concerns, or providing supplementary documentation. Here are some tips for responding to RQAIs:
- Respond Promptly: Timely responses demonstrate your commitment to the review process and can help expedite the overall timeline.
- Provide Clear and Concise Answers: Address the RQAI directly and comprehensively, using clear and well-supported arguments. This typically requires involving subject-matter experts.
- Maintain Open Communication: Keep the regulatory body informed of your progress in addressing the RQAI and be prepared to answer any follow-up questions.
Common Challenges of NDA Submissions
The NDA submission process can be complex and demanding. Here are some common challenges that you may encounter along the way:
- Insufficient Preclinical or Clinical Data: This is not uncommon. However, robust data from preclinical (animal) and clinical (human) trials is vital for demonstrating a drug’s safety and efficacy. Insufficient data or studies with methodological flaws can raise red flags for regulatory bodies and potentially delay approval.
- Manufacturing or Quality Control Issues: Regulatory bodies meticulously assess a drug’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Any deficiencies in these areas can lead to significant delays or even rejection of an NDA submission.
- Inadequate Documentation or Incomplete Submissions: An NDA submission package is a comprehensive document requiring meticulous attention to detail. Missing or incomplete documentation, or failure to adhere to formatting guidelines, can hinder the review process and necessitate revisions. That’s why many companies adapt to work with document formatting / reviewing automation tools to limit the risk of non-compliance.
- Regulatory Concerns or Deficiencies Identified During Review: During the review process, the regulatory body may identify specific concerns or deficiencies regarding the drug’s safety, efficacy, or quality. Addressing these concerns promptly and thoroughly is crucial for moving the application forward.
- Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: Needless to say, the global regulatory landscape for pharmaceuticals is one of the most complex ones. Things change quite often. Not to mention each layer of additional complexity for each different country or region. Understanding the specific requirements and navigating the processes of different regulatory bodies can be challenging. Even if you have successfully completed an NDA submission before…
- Limited Resources: Developing and submitting an NDA can be a resource-intensive process. Gathering years’ worth of data and documentation in a short amount of time…. Smaller companies may have limited financial and human resources to dedicate to comprehensive pre-clinical and clinical trials, data analysis, and assembling a robust NDA package.
- Lack of Internal Expertise: Building an internal team with the necessary expertise in regulatory affairs, clinical research, and drug development can be a challenge, particularly for smaller companies.
Conclusion
The successful marketing of new drugs relies heavily on well-crafted and compliant NDA submissions. Based on being able to present years worth of data and documentation in an accurate, compliant way.
These submissions play a critical role in ensuring patient safety and drug effectiveness by providing regulatory bodies with a comprehensive picture of a new drug’s potential benefits and risks.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the key considerations and best practices for navigating the NDA submission process. From meticulous preparation and adherence to regulatory requirements to effectively responding to feedback from regulatory agencies, a strategic approach is essential for a successful application.
The ever-evolving pharmaceutical landscape demands ongoing commitment to regulatory compliance and patient safety. By understanding the intricacies of the NDA submission process and implementing best practices, companies can bring safe and effective new drugs to market, ultimately improving patient lives.
How DocShifter Can Help
While this guide has provided a general overview of the NDA submission process, navigating the complexities of regulatory compliance can be a significant challenge.
Today, there is automation possible to create fully-compliant Word and PDF documents for your NDA submissions. Without any manual work.
After years’ worth of R&D, you want to compile your submission to market your drug as soon as possible.
DocShifter software automatically generates submission-ready PDFs from your source content. Lightning fast, fully compliant with one or multiple health authorities.
It can also help identify issues in your Word or PDF documents; and automatically fix them. Saving you hundreds of valuable hours in critical NDA submissions. Accelerating your time-to-market by allowing you to focus on what matters most: the content.